Growing under glass
From Allotments4All
Basic Requirements to be considered when growing under glass.
Contents
Temperature & heating
Electric heaters
These are usually very efficient and effective and quite easy to install. There are several types from tubular heaters, fan heaters and warming cables, either air or soil.
Good points
- Clean
- Keeps air circulating
- No fuel storage needed
- Dry heat, reduces the chance of fungus
- Easily controlled e.g. thermostats, timers
Bad points
- Requires electricity which can be expensive to install.
- Expensive to run, although other forms of heating are no longer the cheap alternative that they used to be.
- Possibities of power cuts.
- Chance of damaging the cable run to the greenhouse with a spade etc.
Ventilation
Hydraulic systems that will automatically open and close windows.
Humidity
Pests & Diseases
Light and shading
Hygiene
Feeding
Planting
Planting choices
Growbags and Pots
Directly into the border
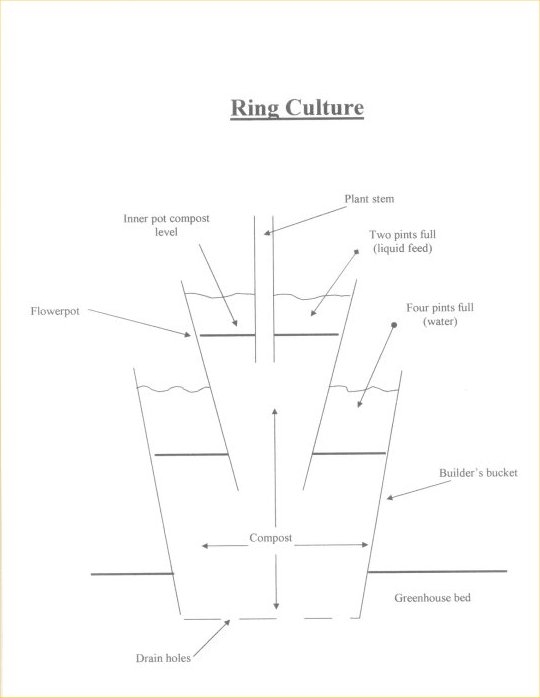
Ring Culture
A shallow trench is dug out in a border, lined with polythene and filled in with gravel (a large gravel filled tray can also be used). A nine-inch bottomless pot is filled with soil, planted with the tomato seedling and placed on the gravel bed.
The tomatoes are watered from the bottom via the gravel bed and fed via the pot. This way the tomatoes have a free draining system with water and feed available to the plants as and when they need to take it up. At the end of the year, remove the plants and pots. Fill a watering can with jaye's fluid, dilute as per the instructions, and water the gravel to kill off any germs and disease. One disease free greenhouse.